1222. Queens That Can Attack the King
Medium
On an 8×8 chessboard, there can be multiple Black Queens and one White King.
Given an array of integer coordinates queens that represents the positions of the Black Queens, and a pair of coordinates king that represent the position of the White King, return the coordinates of all the queens (in any order) that can attack the King.
Example 1:
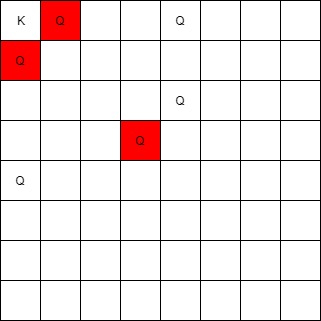
Input: queens = [[0,1],[1,0],[4,0],[0,4],[3,3],[2,4]], king = [0,0]
Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,3]]
Explanation:
The queen at [0,1] can attack the king cause they're in the same row.
The queen at [1,0] can attack the king cause they're in the same column.
The queen at [3,3] can attack the king cause they're in the same diagnal.
The queen at [0,4] can't attack the king cause it's blocked by the queen at [0,1].
The queen at [4,0] can't attack the king cause it's blocked by the queen at [1,0].
The queen at [2,4] can't attack the king cause it's not in the same row/column/diagnal as the king.
Example 2:
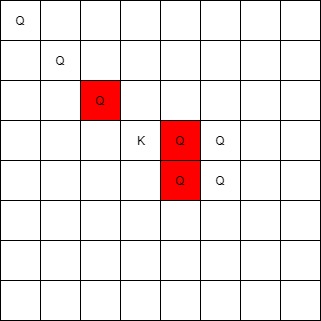
Input: queens = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[3,5],[4,4],[4,5]], king = [3,3]
Output: [[2,2],[3,4],[4,4]]
Example 3:
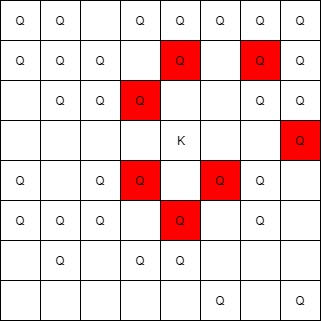
Input: queens = [[5,6],[7,7],[2,1],[0,7],[1,6],[5,1],[3,7],[0,3],[4,0],[1,2],[6,3],[5,0],[0,4],[2,2],[1,1],[6,4],[5,4],[0,0],[2,6],[4,5],[5,2],[1,4],[7,5],[2,3],[0,5],[4,2],[1,0],[2,7],[0,1],[4,6],[6,1],[0,6],[4,3],[1,7]], king = [3,4]
Output: [[2,3],[1,4],[1,6],[3,7],[4,3],[5,4],[4,5]]
Constraints:
1 <= queens.length <= 63queens[i].length == 20 <= queens[i][j] < 8king.length == 20 <= king[0], king[1] < 8- At most one piece is allowed in a cell.
思路
King 最多受到来自 8 个方向的攻击(水平 2,垂直 2,对角 4)。因此开辟一个数组 queens_on_directions 用于存放每个方向上距离 King 最近的可发起攻击的 Queen。
遍历 queens 数组,对其中的每个 queen,首先判断其是否在 king 的八个可被攻击方向上(计算 queen 和 king 的横纵坐标差,并以 -1 表示不可攻击,0 – 7 表示 8 个可攻击方向)。
若可攻击,则判断当前的 queen 和之前此方向上的 queen 哪个距离 king 更近,并更新 queens_on_directions 数组。
遍历完 queens 数组后,返回 queens_on_directions 中的有效 queen。
int get_distance(vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
return abs(a[0] - b[0]) + abs(a[1] - b[1]);
}
int check_attackable(vector<int> queen, vector<int> tgt) {
int horizontal = queen[0] - tgt[0];
int vertical = queen[1] - tgt[1];
if (horizontal == 0) return vertical < 0 ? 0 : 4;
else if (vertical == 0) return horizontal < 0 ? 6 : 2;
else {
if (abs(horizontal) != abs(vertical)) return -1;
else {
if (horizontal < 0) {
return vertical < 0 ? 7 : 5;
}
else {
return vertical < 0 ? 1 : 3;
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> queensAttacktheKing(vector<vector<int>>& queens, vector<int>& king) {
vector<int> null_queen = {-9, -9};
vector<vector<int>> queens_on_directions(8, null_queen);
for (auto queen: queens) {
int attackable = check_attackable(queen, king);
if (attackable == -1) {}
else {
int old_distance = get_distance(queens_on_directions[attackable], king);
int new_distance = get_distance(queen, king);
if (new_distance < old_distance) {
queens_on_directions[attackable] = queen;
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> res;
for (auto queen: queens_on_directions) {
if (queen != null_queen) {
res.emplace_back(queen);
}
}
return res;
}
};
Runtime: 4 ms, faster than 90.89% of C++ online submissions for Queens That Can Attack the King.
Memory Usage: 11.2 MB, less than 55.84% of C++ online submissions for Queens That Can Attack the King.